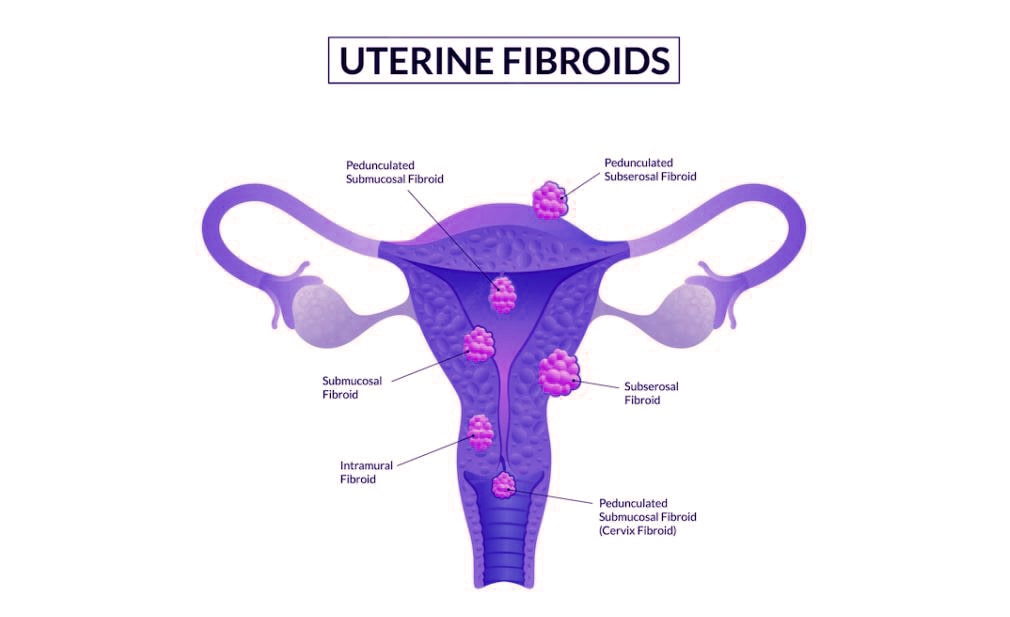
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous uterine growths that commonly appear during childbearing years and grow in and on your uterus. In your pelvis, your uterus is an upside-down pear-shaped organ. Your uterus should be around the size of a lemon. It's also known as the womb, and it's where a kid develops and grows during pregnancy. Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas (lie-o-my-O-muhs) or myomas, are not associated with a higher risk of uterine cancer but almost never develop into cancer.
Uterine fibroids are commonly found by chance during a routine pelvic exam. Your doctor may notice irregularities in the shape of your uterus, which could indicate the presence of fibroids.
Uterine Fibroids Symptoms
Fibroids do not always create symptoms, but when they do, they may cause
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Back pain
- A feeling of fullness in your lower abdomen/bloating.
- Lower back pain
- Frequent urination
- Sex pain.
- Constipation
- Increased abdominal distention (enlargement), giving the appearance of a pregnant stomach.
- Vaginal discharge that is persistent.
Small fibroids rarely require treatment, while bigger fibroids may require medication or surgery.
Uterine Fibroid Diagnosis
Fibroids are frequently identified during a routine evaluation with a women's health practitioner. They can be detected and identified during a pelvic exam, as well as a gynecologic checkup or prenatal care.
- Ultrasonography
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Hysteroscopy
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
- Sonohysterography
- Laparoscopy
Uterine Fibroid Treatments
Treatment for uterine fibroids varies depending on their size, quantity, and location, as well as the symptoms they cause. Small fibroids rarely require treatment, while bigger fibroids may require medication or surgery.
Small fibroids can usually be ignored. Most women don't have any symptoms or concerns related to fibroids at all. Your fibroids will be continuously monitored throughout time, but there is no need to take action right away. Depending on the size and symptoms of your fibroid, your healthcare professional may recommend periodic pelvic exams and ultrasounds. Treatment is normally required if you are having symptoms from your fibroids, such as anemia from excessive bleeding, moderate to severe pain, infertility issues, or urinary tract and bowel problems.
Your appropriate treatment option will also be determined by your long-term fertility goals. Some treatment choices may not be suitable if you wish to have children in the future. When considering treatment choices, tell your healthcare professional about your ideas on fertility and your long-term aspirations.
Some of the Uterine Fibroid Medications are:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain medications
- Iron supplements
- Birth control
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists
- Oral therapies
Fibroid Surgery
When discussing the many forms of fibroid removal surgeries, there are several aspects to consider. Not only may the size, location, and a number of fibroids affect the type of surgery performed, but your plans for future pregnancies can also play a role in deciding on a treatment plan. Some surgical procedures protect the uterus and allow you to conceive in the future, whereas others damage or remove the uterus.
Myomectomy is a technique that allows your doctor to remove fibroids from your uterus without hurting it. Myomectomy comes in a variety of forms. The type of operation that is appropriate for you will be determined by the location of your fibroids, their size, and the number of fibroids you have. The following are examples of myomectomy procedures for removing fibroids:
- Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a process that involves inserting a narrow, flexible tube-like equipment ( scope) into the uterus through the vaginal and cervix. During this surgery, no incisions are made. The scope will be used to cut away the fibroids during the surgery. The fibroids will subsequently be removed by your doctor. - Laparoscopy
Your provider will use a scope to remove the fibroids during this surgery. This treatment, unlike hysteroscopy, requires making a few small incisions in your abdomen. The scope will enter and exist in your body in this manner. With the help of a robot, this surgery can also be completed. - Laparotomy
During a laparotomy, an incision is made in your belly, and the fibroids are removed through this single bigger cut.
If pregnancy is desired, these treatments are not indicated, and there are surgical options to remove the uterus. These procedures can be quite effective, but they almost always result in the prevention of future births. Surgical procedures to eliminate fibroids include:
- Hysterectomy procedure:
Your uterus is removed during a hysterectomy procedure. Fibroids can only be treated through a hysterectomy. The fibroids won't return when your uterus is removed fully, and your symptoms should go away. After a hysterectomy, if your uterus is removed but your ovaries are left in place, you will not experience menopause. If you have large fibroids or are experiencing severe bleeding from your fibroids, this operation may be indicated. When hysteroscopy is recommended, it is best to choose the least invasive procedure possible. Vaginal, laparoscopic, and robotic operations are examples of minimally invasive procedures. - Uterine Fibroid Embolization
An interventional radiologist collaborates with your gynecologist to perform uterine fibroid embolization. Tiny particles are utilized to stop the flow of blood from the uterine artery to the fibroids using a small catheter put in the uterine artery or radial artery. The loss of blood flow causes the fibroids to shrink, which improves your symptoms. - Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a safe and effective treatment for symptomatic uterine fibroids that can be done laparoscopically, transvaginally, or transcervically.
When it comes to Uterine Fibroids, who is at risk?
Several risk factors can increase your chances of acquiring fibroids. These may include the following:
- Obesity and a higher body weight
- Fibroids in Family History
- Not being able to have children.
- Menstruation that begins early
- Menopause occurs later in life.